How Does a Turbocharger Work?
You’ve heard the word “turbo” tossed around a lot, especially by performance car enthusiasts. But all you know is that it means an engine has more “oomph” to it than normal. But what exactly is going on underneath that hood? Let’s open it up and take a look.
It’s All About Better Combustion
Before you can truly appreciate what a turbocharger does for an engine, you need to understand the basics of internal combustion.
Internal combustion engines are “breathing” engines. That is to say, they draw in air and fuel for energy. This energy is realized as power when the air-fuel mixture is ignited. Afterward, the waste created by the combustion is expelled. All of this is typically accomplished in four strokes of the pistons.
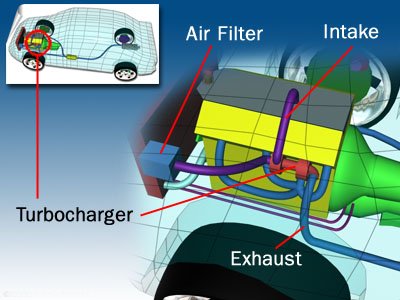
A Tale Of Two Wheels
A turbocharger is basically an air pump. Hot exhaust gases leaving the engine after combustion are routed directly to the turbine wheel side of the turbocharger to make it rotate. That turbine wheel is connected by a shaft to a compressor wheel. As the turbine wheel spins faster and faster, it causes the compressor wheel to also spin quickly. The rotation of the compressor wheel pulls in ambient air and compresses it before pumping it into the engine’s chambers.



Not As Easy As It Looks
The basic principal behind turbocharging is fairly simple, but a turbocharger is a very complex piece of machinery. Not only must the components within the turbocharger itself be precisely coordinated, but the turbocharger and the engine it services must also be exactly matched. If they’re not, engine inefficiency and even damage can be the results. That’s why it’s important to follow correct installation, operating and preventative maintenance procedures




